Testing an Ecommerce Web Component using Cypress

Integration testing examines how components work together within the application. For the CartItem component, we use Cypress to perform end-to-end tests that simulate user interactions and verify the application’s behavior.
This is the third blog post in a trilogy related to vanilla JavaScript Web Components:
- Creating an Ecommerce Web Component from scratch.
- Testing an Ecommerce Web Component using Jest.
- Testing an Ecommerce Web Component using Cypress.
Detailed test cases
Step 1: Testing Environment Setup
Since we are working with a Vanilla JavaScript project, we need to perform some basic setup for our testing environment using Cypress:
- Install Cypress front end testing tool running the
npm install cypress --save-devcommand - Add the following scripts in the
package.jsonfile:"scripts": { "cypress:open": "cypress open", "cypress:run": "cypress run" }, - Verify that the
cypress.config.jsfile has been created and contains the following configuration:const { defineConfig } = require("cypress"); module.exports = defineConfig({ e2e: { setupNodeEvents(on, config) { // implement node event listeners here }, }, }); - Add the following file paths to the
.gitignorefile:# Cypress test artifacts cypress/videos cypress/screenshots
Step 2: Reviewing Ecommerce App Functionality
Integration testing examines how components work together within the application. Therefore, it’s essential to review the overall functionality to gain a clear understanding of the tests to perform.
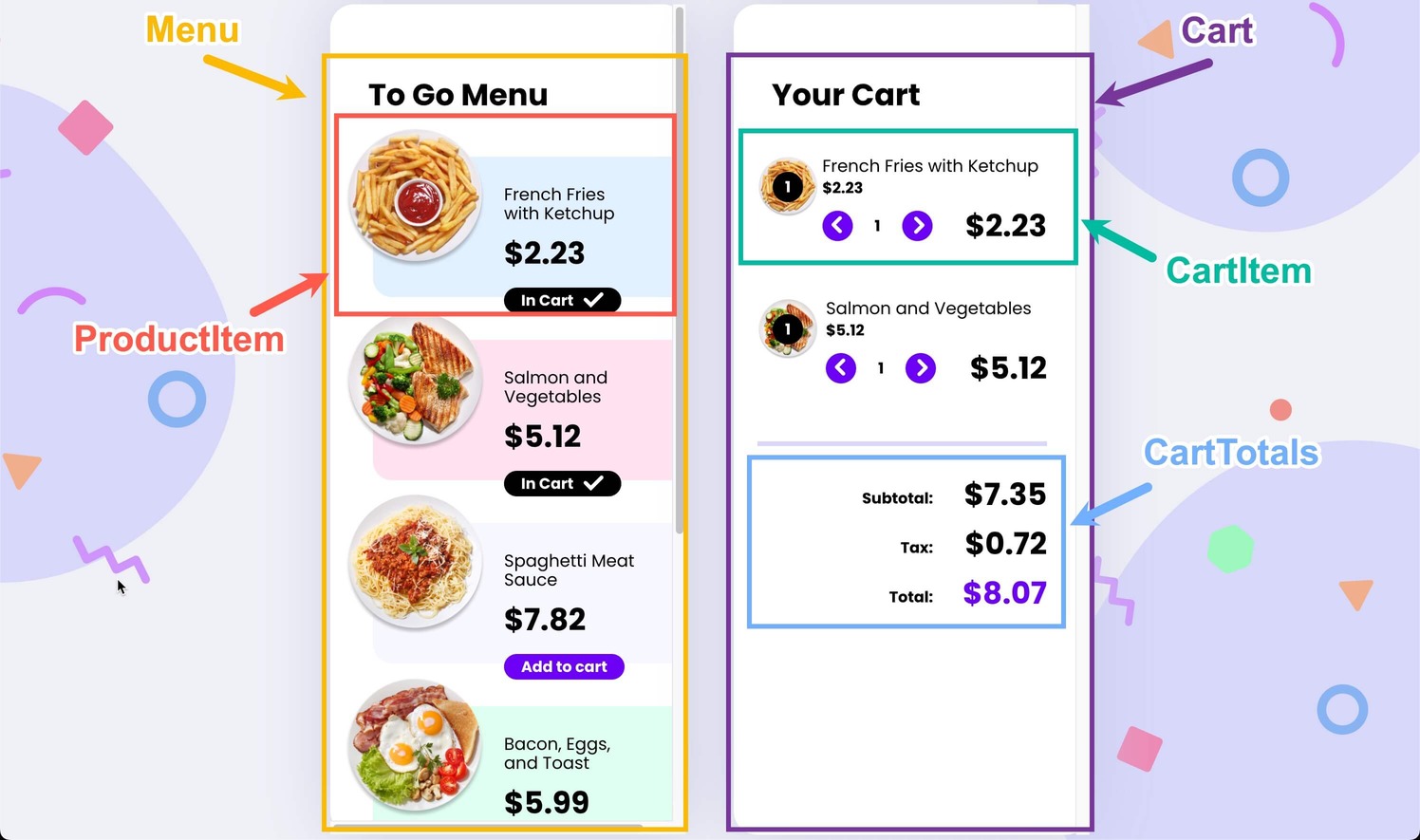
In the following image, we can identify the different components of the ecommerce app. Remember, we have been focusing solely on the CartItem component:
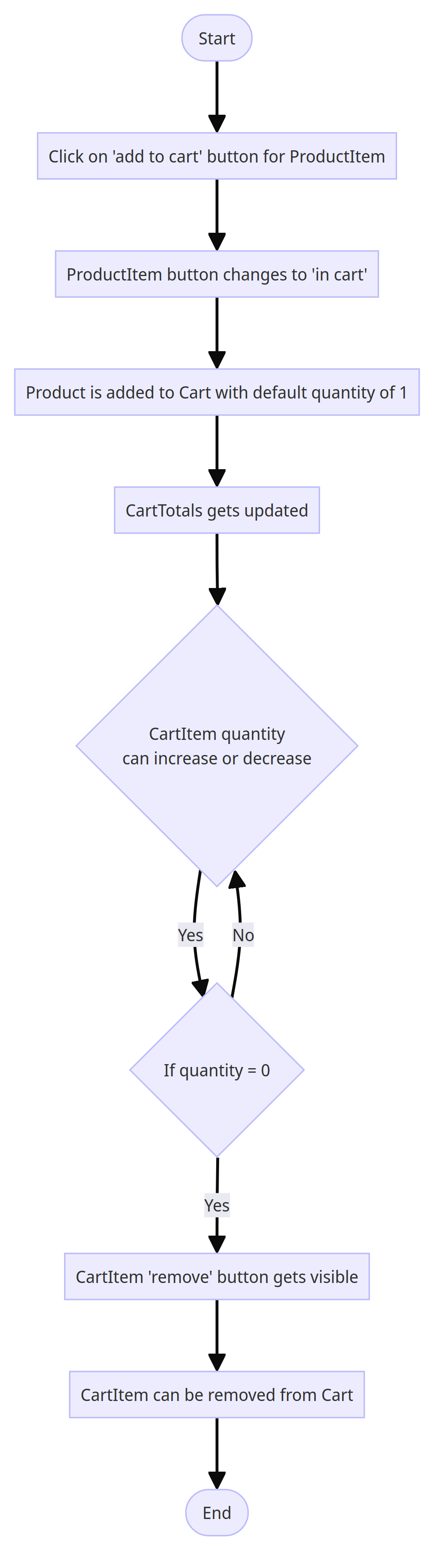
Now that we have a better understanding of the app, we can easily comprehend the next functionality flowchart:
Ecommerce flowchart
Step 3: One Item in Cart Interaction Testing Setup
Each test begins with defining the constants values, finding the price text and the button of the first ProductItem in the Menu component and then clicking on it:
let itemPrice;
const taxRate = 0.0975;
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit('/')
.get('[data-testid="menu"]').find('.price').first().invoke('text')
.then((text) => {
itemPrice= parseFloat(text.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
})
.get('[data-testid="menu"] button').first().click({ force: true })
})Step 4: Testing One Item in Cart Interaction
The first test suite simulates adding an item to the cart and verifying that the item appears in the cart summary with the correct details:
describe('Add item to cart', () => {
it('should add an item to the cart', () => {
cy.get('[data-testid="menu"] button').first().should('have.class', 'in-cart')
.get('[data-testid="cart-summary"] li').should('have.length', 1)
})
it('should update totals when an item is added to the cart', () => {
cy.get('[data-testid="menu"]').find('.price').first().invoke('text')
.then((text) => {
itemPrice= parseFloat(text.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
})
.then(() => {
// Calculate expected tax and total
const expectedTax = itemPrice * taxRate;
const expectedTotal = itemPrice + expectedTax;
// Assert that the subtotal is equal to the item price
cy.get('[data-testid="subtotal"]').invoke('text')
.then((subTotalText) => {
const subTotal = parseFloat(subTotalText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(subTotal).to.equal(itemPrice);
})
// Calculate expected tax and total
cy.get('[data-testid="tax"]').invoke('text')
.then((taxText) => {
const displayedTax = parseFloat(taxText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(displayedTax).to.closeTo(expectedTax, 0.01);
})
// Retrieve and assert the displayed total value
cy.get('[data-testid="total"]').invoke('text')
.then((totalText) => {
const displayedTotal = parseFloat(totalText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(displayedTotal).to.closeTo(expectedTotal, 0.01);
})
})
})
})The second test suite cover increasing and decreasing an item’s quantity within the Cart, verifying that the Cart updates to reflect these changes accurately:
describe('Update item in cart', () => {
it('should increase item quantity and cart total values', () => {
cy.get('.increase').click()
.then(() => {
const newQuantity = 2;
const expectedSubTotal = itemPrice * newQuantity;
const expectedTax = expectedSubTotal * taxRate;
const expectedTotal = expectedSubTotal + expectedTax;
// Assert that the subtotal is equal to the item price
cy.get('[data-testid="subtotal"]').invoke('text')
.then((subTotalText) => {
const subTotal = parseFloat(subTotalText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(subTotal).to.equal(expectedSubTotal);
})
// Calculate expected tax and total
cy.get('[data-testid="tax"]').invoke('text')
.then((taxText) => {
const displayedTax = parseFloat(taxText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(displayedTax).to.closeTo(expectedTax, 0.01);
})
// Retrieve and assert the displayed total value
cy.get('[data-testid="total"]').invoke('text')
.then((totalText) => {
const displayedTotal = parseFloat(totalText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(displayedTotal).to.closeTo(expectedTotal, 0.01);
})
})
})
it('should decrease item quantity and cart total values', () => {
cy.get('.decrease').click()
.then(() => {
const newQuantity = 0;
const expectedSubTotal = itemPrice * newQuantity;
const expectedTax = expectedSubTotal * taxRate;
const expectedTotal = expectedSubTotal + expectedTax;
// Assert that the subtotal is equal to the item price
cy.get('[data-testid="subtotal"]').invoke('text')
.then((subTotalText) => {
const subTotal = parseFloat(subTotalText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(subTotal).to.equal(expectedSubTotal);
})
// Calculate expected tax and total
cy.get('[data-testid="tax"]').invoke('text')
.then((taxText) => {
const displayedTax = parseFloat(taxText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(displayedTax).to.closeTo(expectedTax, 0.01);
})
// Retrieve and assert the displayed total value
cy.get('[data-testid="total"]').invoke('text')
.then((totalText) => {
const displayedTotal = parseFloat(totalText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(displayedTotal).to.closeTo(expectedTotal, 0.01);
})
})
})
})The third test suite ensures that an item can be removed from the cart, and the Cart updates accordingly:
describe('Remove item from cart', () => {
it('should remove an item from the cart', () => {
cy.get('.decrease').click()
.get('.remove').click({ force: true })
.get('[data-testid="cart-summary"] li').should('have.length', 0)
.get('[data-testid="menu"] button').first().should('not.have.class', 'in-cart')
})
it('should update totals when an item is removed from the cart', () => {
cy.get('.decrease').click()
.get('.remove').click({ force: true })
.then(() => {
cy.get('[data-testid="subtotal"]').invoke('text')
.then((subTotalText) => {
const subTotal = parseFloat(subTotalText.replace(/[^0-9.-]+/g, ""));
expect(subTotal).to.equal(0);
})
})
})
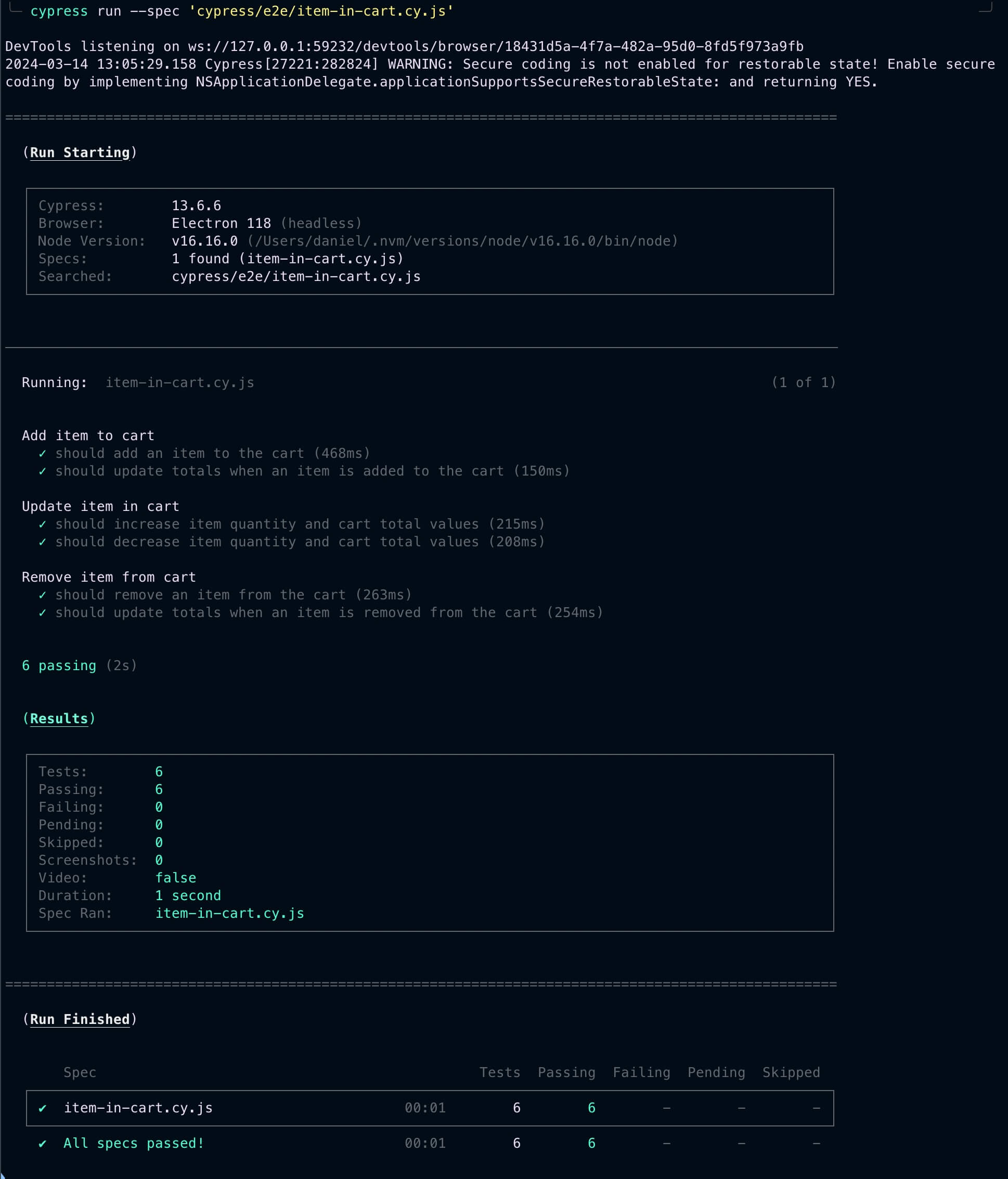
})That’s it!. We now have a complete integration test suite for our CartItem Web Component. The results can be seen running the cypress run --spec 'cypress/e2e/item-in-cart.cy.js' command in the terminal, where the spec path should be an absolute path or can be relative to the current working directory:
Next Steps: Testing Multiple Items in Cart Interaction
Testing the functionality of adding and removing multiple items in the Cart component is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of the ecommerce application.
This kind of testing helps uncover potential issues related to item interactions, quantity adjustments, and total calculations, providing a comprehensive evaluation of the cart functionality.
For more details on the test suite for multiple cart items, visit the codebase in the following link: click here
Conclusion
These integration tests validate the CartItem component’s interaction with other parts of the application, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Through these three blog posts, we’ve explored the creation, unit testing, and integration testing of the CartItem web component, demonstrating the importance of each step in developing reliable and maintainable web applications.