Creating an Ecommerce Web Component from scratch

In this post, we’ll explore how to create a web component for cart items in an e-commerce application. Web components allow for encapsulation and reusability, making them ideal for such features.
This is the first blog post in a trilogy related to vanilla JavaScript Web Components:
- Creating an Ecommerce Web Component from scratch.
- Testing an Ecommerce Web Component using Jest.
- Testing an Ecommerce Web Component using Cypress.
Introduction
The ecommerce app implementation is shown in the image below. We are going to focus on the CartItem Web Component, located to the right, which renders inside the Cart container.
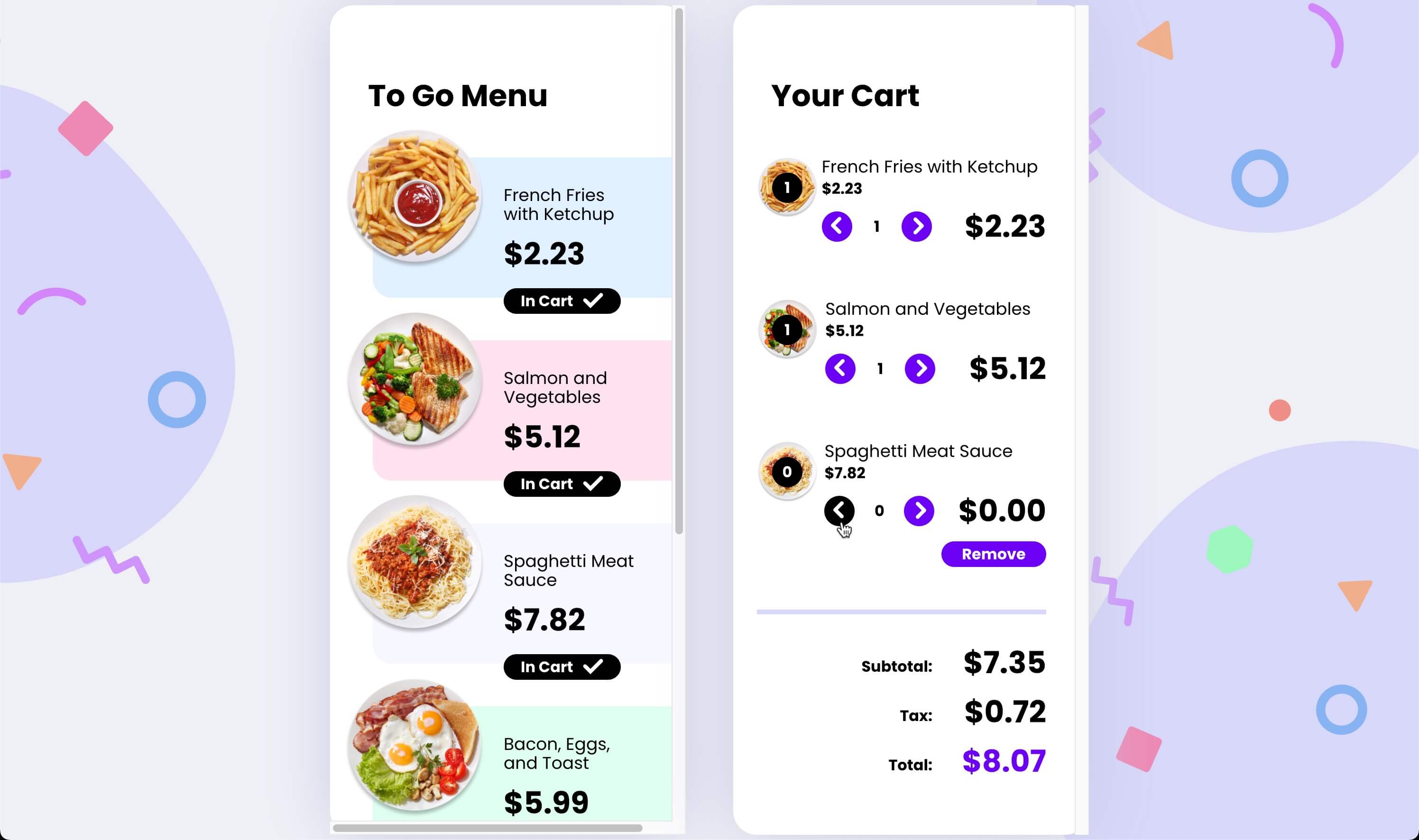
Feel free to explore the entire ecommerce codebase by visiting the GitHub repository. To try the app in action, you can click here.
Step 1: Define the CartItem Class
First, we define the CartItem class extending from HTMLElement. This class will manage the cart item’s data and render its HTML structure:
export class CartItem extends HTMLElement {
// Define the private state variable
#state;
// Constructor takes an object with properties like:
// 'name', 'image', 'alt', 'quantity', 'price', and 'subTotal'
constructor({ name, image, alt, quantity, price, subTotal }) {
// Define properties for the element
super();
// Initialize properties with the values passed in the constructor
this.name = name;
this.image = image;
this.alt = alt;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.price = price;
this.isRemoveCTAHidden = true;
// Set 'subTotal' to the provided value or default to the product price
this.subTotal = subTotal ?? this.price;
// Initialize the 'state' object with the initial values of the properties
this.#state = {
quantity: this.quantity,
subTotal: this.subTotal
}
}
}Step 2: Implementing Getters and Setters for internal state
Next, we implement getters and setters to access and update the internal state of the CartItem component. This allows controlled access to the component’s data:
// Getter method to get the value of a property in the state object
getState(path) {
return this.#state[path];
}
// Setter method to set the value of a property in the state object
setState(path, value) {
if (this.#state[path] !== value) {
this.#state = { ...this.#state, [path]: value };
}
}Step 3: Implementing the render function
The render function manages the HTML structure to append to the selected DOM node. Here, we’re using template literals since it’s a basic component.
Keep in mind that the numberToPrice function could incorporate custom logic for price formatting.
Additionally, we’ve included a ternary operator to toggle the hidden class in the remove button. This allows us to show or hide the button based on the isRemoveCTAHidden prop, which is set by default to true:
For more details on the CSS styles, please check out the codebase by visiting the GitHub repository.
// Render method to create the initial HTML structure of the component
render() {
this.innerHTML = `
<li data-name="${this.name}">
<div class="plate">
<img src="images/${this.image}" alt="${this.alt}" class="plate" />
<div class="quantity">${this.getState('quantity')}</div>
</div>
<div class="content">
<p class="menu-item">${this.name}</p>
<p class="price">${numberToPrice(this.price)}</p>
</div>
<div class="quantity__wrapper">
<button class="decrease">
<img src="images/chevron.svg" />
</button>
<div class="quantity">${this.getState('quantity')}</div>
<button class="increase">
<img src="images/chevron.svg" />
</button>
</div>
<div class="subtotal">${numberToPrice(this.getState('subTotal'))}</div>
<button class="remove ${this.isRemoveCTAHidden ? 'hidden' : ''}">Remove</button>
</li>
`;
}Step 4: Implementing the increaseQuantity and decreaseQuantity methods
In this step, we focus on implementing the increaseQuantity and decreaseQuantity methods within the CartItem component. These methods handle the functionality of adjusting the quantity of an item in the cart and updating the subtotal accordingly:
// Private method to increase the quantity and update the subTotal property in the state object.
#increaseQuantity() {
// Get the current quantity value from the state
const currentValue = this.getState('quantity');
// Calculate the new quantity by incrementing the current value
const newValue = currentValue + 1;
// Update the quantity and subTotal properties in the state
this.setState('quantity', newValue);
this.setState('subTotal', newValue * this.price);
// Hide the remove button if the quantity is greater than 0
this.isRemoveCTAHidden = true;
// Re-render the cart item with the updated values
this.render();
}
// Private method to decrease the quantity and update the subTotal property in the state object.
#decreaseQuantity() {
// Get the current quantity value from the state
const currentValue = this.getState('quantity');
// Calculate the new quantity by decrementing the current value
const newValue = currentValue - 1;
// Check if the new quantity is greater than 0 before updating
if (currentValue > 0) {
this.setState('quantity', newValue);
this.setState('subTotal', newValue * this.price);
}
// Update the visibility of the remove button based on the quantity
if (this.getState('quantity') === 0) {
this.isRemoveCTAHidden = false;
}
// Re-render the cart item with the updated values
this.render();
}Step 5: Dispatching custom events in the component
In this step, we will explore the removeFromCartEvent and quantityChangeEvent methods in the CartItem component, responsible for dispatching custom events related to cart actions:
By utilizing these methods to dispatch custom events, the CartItem component can communicate changes in item quantities and removal actions effectively within the application, enhancing the overall user experience and functionality.
// Private method to dispatch a custom event when 'Remove from cart' button is clicked
#removeFromCartEvent() {
// Dispatch a custom event to remove the item from the cart
document.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent('remove-from-cart', {
detail: { name: this.name }
}));
}
// Private method to dispatch custom events for 'Decrease quantity'
// and 'Increase quantity'
#quantityChangeEvent(event) {
// Prepare product details for the custom event
const productDetails = {
name: this.name,
quantity: this.quantity,
price: this.price
};
// Dispatch custom events based on the event type
if (event === 'decrease-quantity') {
// Dispatch the decreaseQuantity event with product details
document.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent('decrease-quantity', {
detail: productDetails
}));
}
if (event === 'increase-quantity') {
// Dispatch the increaseQuantity event with product details
document.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent('increase-quantity', {
detail: productDetails
}));
}
}Step 6: Implementing the click event handler
In this step, we will delve into the handleButtonClick method of the CartItem component, which manages the actions triggered by clicking on buttons within the cart item:
// Private method to handle click events on the remove,
// decrease, and increase buttons
#handleButtonClick(event) {
// Extract the target element from the event
const { target } = event;
// Find the closest button element and get its class list
const targetClassList = target.closest('button').classList;
// Check the class of the clicked button and perform corresponding actions
if (targetClassList.contains('remove')) {
// If the button is for removing, trigger the remove event
this.#removeFromCartEvent();
} else if (targetClassList.contains('decrease')) {
// If the button is for decreasing quantity, decrease the quantity
// and trigger the decrease quantity event
this.#decreaseQuantity();
this.#quantityChangeEvent('decrease-quantity');
} else if (targetClassList.contains('increase')) {
// If the button is for increasing quantity, increase the quantity
// and trigger the increase quantity event
this.#increaseQuantity();
this.#quantityChangeEvent('increase-quantity');
}
}Step 7: Implementing the connectedCallback and disconnectedCallback
The connectedCallback method is where we render the cart item and attach event listeners. Here, we dynamically create the HTML structure and append it to the DOM.
The disconnectedCallback method is where we detach event listeners when the component is removed from the DOM to avoid memory leaks:
// ConnectedCallback is called when the element is inserted into the DOM
connectedCallback() {
// Render the initial state
this.render();
// Add event listeners for remove, decrease, and increase buttons
this.addEventListener('click', this.#handleButtonClick)
}
// DisconnectedCallback is called when the element is removed from the DOM
disconnectedCallback() {
// Remove previously added event listeners
this.removeEventListener('click', this.#handleButtonClick)
}Step 8: Registering the custom element
Finally, we register the custom element using window.customElements.define:
window.customElements.define('cart-item', CartItem);That’s it!. We now have a fully functional CartItem Web Component to be integrated in the ecommerce app.
Click on the collapsible section to see the entire code:
cartItem.js
export class CartItem extends HTMLElement {
#state;
constructor({ name, image, alt, quantity, price, subTotal }) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.image = image;
this.alt = alt;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.price = price;
this.isRemoveCTAHidden = true;
this.subTotal = subTotal ?? this.price;
this.#state = {
quantity: this.quantity,
subTotal: this.subTotal
}
}
getState(path) {
return this.#state[path];
}
setState(path, value) {
if (this.#state[path] !== value) {
this.#state = { ...this.#state, [path]: value };
}
}
connectedCallback() {
this.render();
this.addEventListener('click', this.#handleButtonClick)
}
disconnectedCallback() {
this.removeEventListener('click', this.#handleButtonClick)
}
#handleButtonClick(event) {
const { target } = event;
const targetClassList = target.closest('button').classList;
if (targetClassList.contains('remove')) {
this.#removeFromCartEvent();
} else if (targetClassList.contains('decrease')) {
this.#decreaseQuantity();
this.#quantityChangeEvent('decrease-quantity');
} else if (targetClassList.contains('increase')) {
this.#increaseQuantity();
this.#quantityChangeEvent('increase-quantity');
}
}
#increaseQuantity() {
const currentValue = this.getState('quantity');
const newValue = currentValue + 1;
this.setState('quantity', newValue);
this.setState('subTotal', newValue * this.price);
this.isRemoveCTAHidden = true;
this.render();
}
#decreaseQuantity() {
const currentValue = this.getState('quantity');
const newValue = currentValue - 1;
if (currentValue > 0) {
this.setState('quantity', newValue);
this.setState('subTotal', newValue * this.price);
}
if (this.getState('quantity') === 0) {
this.isRemoveCTAHidden = false;
}
this.render();
}
#removeFromCartEvent() {
document.dispatchEvent(CartEvents.removeFromCart(this.name));
}
#quantityChangeEvent(event) {
const productDetails = {
name: this.name,
quantity: this.quantity,
price: this.price
};
if (event === 'decrease-quantity') {
document.dispatchEvent(CartEvents.decreaseQuantity(productDetails));
}
if (event === 'increase-quantity') {
document.dispatchEvent(CartEvents.increaseQuantity(productDetails));
}
}
render() {
this.innerHTML = `
<li data-name="${this.name}">
<div class="plate">
<img src="images/${this.image}" alt="${this.alt}" class="plate" />
<div class="quantity">${this.getState('quantity')}</div>
</div>
<div class="content">
<p class="menu-item">${this.name}</p>
<p class="price">${numberToPrice(this.price)}</p>
</div>
<div class="quantity__wrapper">
<button class="decrease">
<img src="images/chevron.svg" />
</button>
<div class="quantity">${this.getState('quantity')}</div>
<button class="increase">
<img src="images/chevron.svg" />
</button>
</div>
<div class="subtotal">${numberToPrice(this.getState('subTotal'))}</div>
<button class="remove ${this.isRemoveCTAHidden ? 'hidden' : ''}">Remove</button>
</li>
`;
}
}
window.customElements.define('cart-item', CartItem);Next steps
In order to use this component in other apps or directly in the HTML with the custom <cart-item></cart-item> tag, we need to make some changes:
- Modify the constructor for having only the
super()method and the shadow DOM withmode: opento encapsulate the CSS styles - Adding the
static get observedAttributes()method for observing attributes - Adding the
attributeChangedCallbackmethod for responding to observed attributes changes - Using an html
templatefor storing the HTML structure - Adding CSS styling within a
<style></style>tag in a newgetStyles()method and executing it inside thetemplate - Appending the custom
templateto theshadowRootfor rendering
For more details, refer to the Web Components official documentation.
Conclusion
This approach to creating the CartItem component encapsulates its functionality and presentation, making it a reusable and maintainable part of the application’s UI.